We have developed a proprietary technology platform capable of rapidly degrading immunoglobulin G (IgG). This platform employs a globally leading low-pre-existing antibody IgG-degrading enzyme, which, when administered intravenously, can completely eliminate total IgG from plasma and tissues.
IgG is the main component of immunoglobulins in human serum, accounting for about 10-20% of total serum protein. Under normal conditions, IgG protects the body from foreign pathogens. However, in certain disease states, such as IgG-type multiple myeloma or autoimmune diseases caused by pathogenic IgG (e.g., Goodpasture syndrome, Guillain-Barré syndrome, myasthenia gravis), IgG becomes a pathogenic factor.
Even normal IgG can impede life-saving acute treatments for some patients. In allogeneic or xenogeneic organ transplants, IgG in the body recognizes non-self antigens in donor tissue, activating the immune system and leading to rejection. In gene therapy based on viral vectors, IgG can neutralize the vectors, rendering them ineffective.
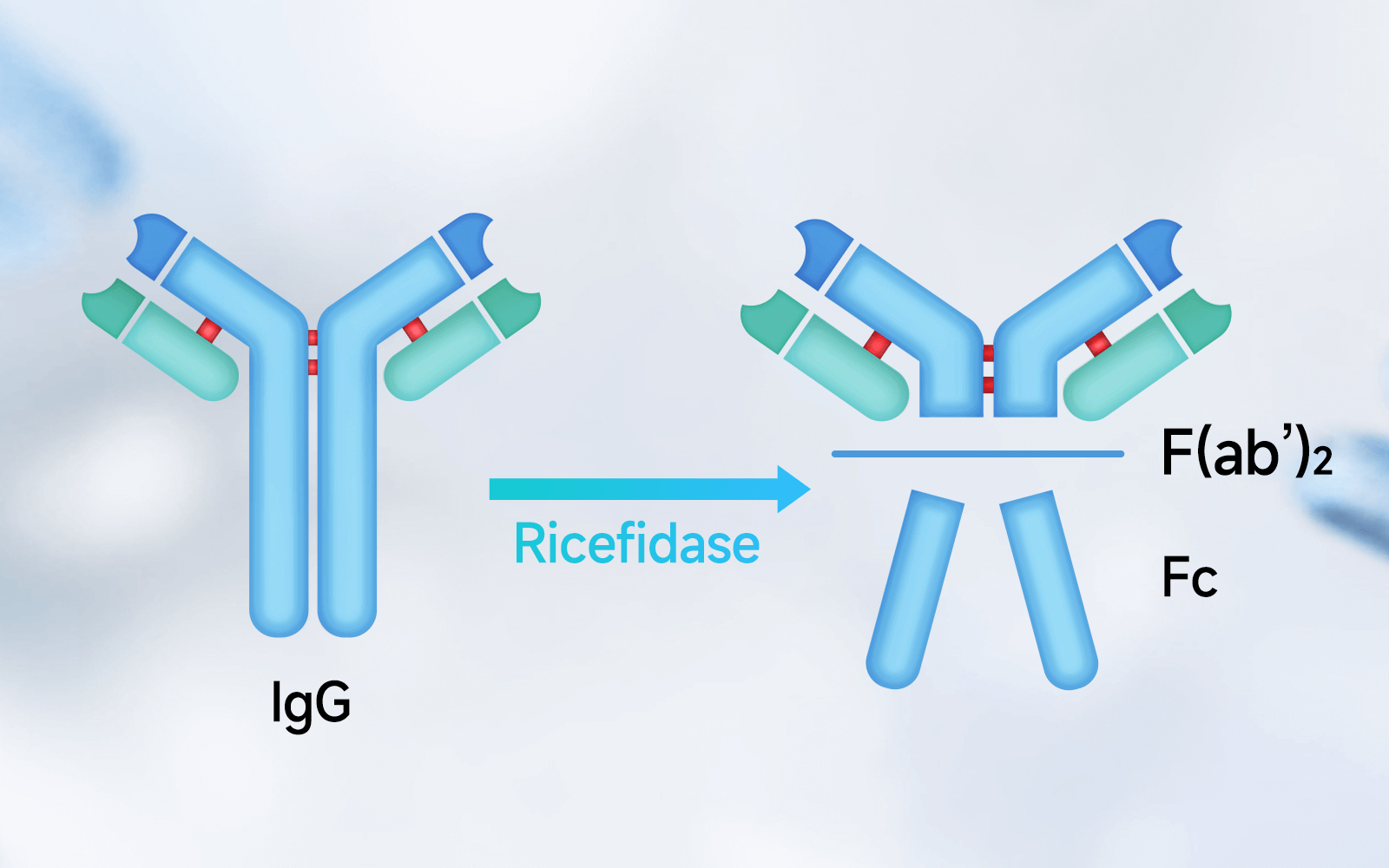
For such large quantities of pathogenic or treatment-interfering IgG, conventional medical management methods are slow and costly. Ricefidase is a globally leading next-generation IgG-degrading enzyme, derived from an enzyme of Streptococcus pyogenes, which does not infect humans. It was independently developed and modified through our proprietary design. Ricefidase specifically degrades the lower hinge region of IgG, rendering it inactive.
Phase I clinical trials conducted in New Zealand and China have demonstrated that within 1 to 2 hours of Ricefidase administration, nearly all IgG in serum and tissues of the subjects was cleaved by the enzyme. The cleaved fragments are unable to mediate Fc-dependent pathological mechanisms, thereby preventing and inhibiting adverse immune reactions such as IgG-induced complement activation, cell killing, and cell activation.
Compared to Imlifidase, which has a high pre-existing antibody rate of over 85% and is approved for use in Europe, Ricefidase has a lower pre-existing antibody rate of less than 20% and exhibits low immunogenicity. Ricefidase also expands the treatment window and holds broader therapeutic potential for conditions such as autoimmune diseases requiring repeated administration, maintenance therapy post-sensitizing organ transplantation, gene therapy, and the treatment of IgG-type multiple myeloma.
In March 2022, Ricefidase received approval from New Zealand's Medsafe to initiate Phase I clinical trials.
In May 2022, Ricefidase obtained FDA clinical trial approval for the treatment of a broad category of autoimmune diseases caused by pathogenic auto-IgG.
In August 2022, Ricefidase received NMPA clinical trial approval for desensitization therapy in highly sensitized kidney transplant patients.
In April 2023, Ricefidase completed Phase I clinical trials in China and New Zealand (CTR20222595/NCT05274659).
In August 2024, Ricefidase received NMPA clinical trial approval for the treatment of anti-GBM disease.
In November 2024, Ricefidase's desensitization therapy for highly sensitized kidney transplant patients was included in the NMPA's "Breakthrough Therapy Designation List."
In December 2024, Ricefidase completed Phase II clinical trials for desensitization therapy in highly sensitized kidney transplant patients in China (CTR20234137).
In April 2025, Ricefidase received NMPA clinical trial approval for the treatment of GBS disease.
In July 2025, Ricefidase's application for anti-GBM disease treatment was included in the NMPA's "Breakthrough Therapy Designation List."
In August 2025, Ricefidase initiated Phase III clinical trials for desensitization therapy in highly sensitized kidney transplant patients in China (CTR20252973).
In October 2025, Ricefidase completed Phase II clinical trials for anti-GBM disease in China (NCT06607016).
In November 2025, Ricefidase initiated Phase II clinical trials for GBS disease in China (CTR20253992).
In November 2025, Ricefidase began preparations in China for a Phase III clinical trial for anti-GBM disease.

Our production process complies with current GMP requirements, and the production scale during clinical phases meets future commercialization needs.